Журнал «Медицина неотложных состояний» Том 21, №7, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Диференційний підхід при лікуванні пацієнтів із поєднаними переломами ключиці та ребер
Авторы: Бур’янов О.А., Кваша В.П., Кравчук М.В., Мясніков Д.В.
Національний медичний університет імені О.О. Богомольця, м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Медицина неотложных состояний
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
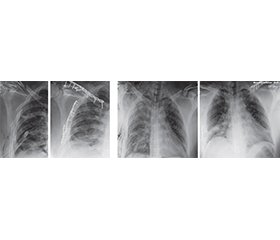
Актуальність. Серед домінуючих пошкоджень на увагу заслуговують поєднані пошкодження грудної клітки та ключиці. Травми грудної клітки є одним з основних чинників летальності у постраждалих як при ізольованих, так і при поєднаних пошкодженнях. У пацієнтів із множинними травмами, які отримали тупу травму грудної клітки, найбільш поширеними пошкодженнями є переломи ребер (86 %), переломи ключиці (19 %) або комбінація цих ушкоджень (19 %). Доведено, що переломи ключиці й ребер є маркерами тяжкості травми грудної клітки. Поєднані переломи ключиці та множинні переломи, особливо верхніх ребер, можуть призвести до тяжких деформацій грудної клітки й порушення функції у плечовому суглобі. Мета: поліпшити результати лікування пацієнтів із поєднаними пошкодженнями ключиці та грудної клітки шляхом впровадження сучасних патогенетично обґрунтованих хірургічних технологій. Матеріали та методи. Клінічне дослідження базується на обстеженні й лікуванні 47 пацієнтів із поєднаними переломами ключиці та ребер за період 2015–2024 рр. Середній вік пацієнтів становив 41,5 ± 11,9 року. Пацієнти були розподілені на дві групи: основна — 23 пацієнти, порівняльна — 24 пацієнти. Результати. Серед 47 пацієнтів із поєднаними переломами ключиці й ребер превалювали постраждалі чоловічої статі — 43 (91,5 %); відповідно, кількість травмованих жіночої статі становила 4 (8,5 %). Серед чинників травмогенезу превалюють дорожньо-транспортні пригоди: до 53,2 % випадків серед пацієнтів чоловічої статі та до 6,4 % — жіночої. Пацієнти основної групи, до яких застосовувався оперативний метод лікування (металоостеосинтез), мали статистично доведені кращі показники щодо виникнення респіраторного дистрес-синдрому (26,1 проти 54,2 % у групі консервативного лікування), післятравматичної пневмонії (33,3 проти 61,5 %), меншу потребу у штучній вентиляції легень (10,6 ± 8,4 проти 16,7 ± 7,9 доби) та коротший термін перебування у відділенні інтенсивної терапії (14,6 ± 10,6 проти 23,6 ± 10,2 доби). Висновки. 1. Сучасна концепція лікування пацієнтів із поєднаними пошкодженнями ключиці та ребер характеризується протилежними поглядами щодо вибору методу лікування й обґрунтування показань до їх застосування. 2. Пацієнти основної групи, до яких застосовано оперативний метод лікування (металоостеосинтез), мали статистично доведені ліпші показники щодо виникнення респіраторного дистрес-синдрому, післятравматичної пневмонії, меншу потребу у штучній вентиляції легень і коротший термін перебування у відділенні інтенсивної терапії.
Background. Among the dominant injuries, combined trauma to the chest and clavicle deserve attention. Chest injuries are one of the main factors of mortality in victims, both in isolated and combined injuries. In patients with multiple injuries who sustained blunt chest trauma, the most common lesions are rib fractures (86 %), clavicle fractures (19 %), or a combination of these injuries (19 %). It has been proven that clavicle and rib fractures are markers of the severity of chest trauma. Combined clavicle fractures and multiple fractures, especially of the upper ribs, can lead to severe chest deformities and dysfunction in the shoulder joint. The purpose was to improve the treatment outcomes of patients with combined injuries of the clavicle and chest by implementing modern pathogenetically based surgical technologies. Materials and methods. The clinical study is based on the examination and treatment of 47 patients with combined fractures of the clavicle and ribs from 2015 to 2024. Their average age was 41.5 ± 11.9 years. The patients were divided into two groups: the main one included 23 people and the comparative group consisted of 24 patients. Results. Among 47 patients with combined fractures of the clavicle and ribs, male victims prevailed — 43 (91.5 %), the rest 4 (8.5 %) people were females. Among the factors of traumatogenesis, road traffic accidents prevail: up to 53.2 % of cases among male patients, and up to 6.4 % of cases among females. Patients in the main group who underwent surgical treatment (metal osteosynthesis) had statistically proven better rates of respiratory distress syndrome (26.1 vs. 54.2 % in the conservative treatment group), post-traumatic pneumonia (33.3 vs. 61.5 %), less need for mechanical ventilation (10.6 ± 8.4 vs. 16.7 ± 7.9 days), and shorter length of stay in the intensive care unit (14.6 ± 10.6 vs. 23.6 ± 10.2 days). Conclusions. 1. The modern concept of treatment of patients with combined injuries of the clavicle and ribs is characterized by opposing views on the choice of therapeutic method and justification of indications for its use. 2. Patients in the main group who underwent surgical treatment (metal osteosynthesis) had statistically proven better indicators regarding the occurrence of respiratory distress syndrome, post-traumatic pneumonia, a lower need for mechanical ventilation, and a shorter stay in the intensive care unit.
політравма; поєднані переломи ключиці та ребер; лікування
polytrauma; combined fractures of the clavicle and ribs; treatment
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Syafiq Basalamah, Harry Jonathan, Ilham Suryo Wibowo Antono. Characteristic of musculskeletal trauma patients admitted to a trauma center in central Yava-Indonesia. International Journal of Medical Reviews and Case Reports. 2021;5(1):107-110. doi: 10.5455/IJMRCR.Musculoskeletal-Trauma-java.
- Sawe H.R., Reynolds T.A., Weber E.J. et al. Trauma care and capture rate of variables of World Health Organisation data set for injury at regional hospitals in Tanzania: first steps to a national trauma registry. 2020;20(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12873-020-00325-y.
- Zsolt J. Balogh. Polytrauma: It is a disease. Injury. 2022;53:1727-1729. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2022.05.001 0020-1383.
- Driessen M.L.S., Sturms L.M., van Zwet E.W. et al. Evaluation of the Berlin polytrauma definition: A Dutch nationwide observational study. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2021;90(4):694-699. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000003071.
- Yeates E.O., Grigorian A., Nahmias J. et al. Isolated thoracic injury patients with rib fractures undergoing rib fixation have improved mortality. J Surg Res. 2021;262:197-202. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2021.01.016.
- Бур’янов О.А., Кравчук М.В., Кваша В.П., Канзюба А.І. Поєднані пошкодження ключиці та грудної клітки: сучасні погляди на діагностику та лікування. Науковий вісник Ужгородського університету, серія «Медицина». 2025;1(71):10-16. doi: 10.32782/2415-8127.2025.71.2.
- van der Linde R.A., van Helden S., Woltz S. et аl. What are the long-term patient-reported and clinical outcomes after la-teral clavicle fractures? A cross-sectional study of 619 patients. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2023 Feb;49(1):289-298. doi: 10.1007/s00068-022-02062-2.
- Dehghan N., Nauth A., Schemitsch E. et аl. Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society and the Unstable Chest Wall RCT Study Investigators. Operative vs Nonoperative Treatment of Acute Unstable Chest Wall Injuries: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Surg. 2022;157(11):983-990. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2022.4299.
- Murphy A., Molinari A., Rasuli B. et al. AO classification of clavicle fractures. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 12 Dec 2024). doi: 10.53347/rID-74186.
- Liu L.T., Chen J.C., Yang T.C. et аl. Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis with Mini-Open Technique and Supraclavicular Nerve Preservation Reduces Postoperative Numbness in Acute Displaced Midshaft Clavicle Fracture. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024;60(10):1669. doi: 10.3390/medicina60101669.
- Shakya S., Wen Y., Wen X. Long C. et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) with mini-open technique versus open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) in the treatment of displaced midclavicular fracture: a retrospective study. J Orthop Traumatol. 2025;26(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s10195-025-00865-8.
- Matsubara Y., Nakamura Y., Sasashige Y. et al. Long-term conservative treatment outcomes for midshaft clavicle fractures: a 10-to-30-year follow-up. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):952. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-04450-9.
- Charles S.J., Chen S.R., Mittwede P. et al. Risk factors for complications and reoperation following operative management of displaced midshaft clavicle fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2022;31(10):498-506. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2022.03.016.
- Ling K., Van Helmond T., Mehta N. et al. Smoking Is Mar–kedly Associated With 30-Day Readmission and Revision Surgery After Surgical Treatment of Clavicle Fracture. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2024;8(7):e23.00278. doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-23-00278.
- Uittenbogaard S.J., van Es L.J.M., den Haan C. et аl. Outcomes, Union Rate, and Complications After Operative and Nonoperative Treatments of Neer Type II Distal Clavicle Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of 2284 Patients. The American Journal of Sports Medicine. 2023;51(2):534-544. doi: 10.1177/03635465211053336.
- Singh A., Schultzel M., Fleming J.F. et аl. Complications after surgical treatment of distal clavicle fractures. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019;105(5):853-859. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2019.03.012.
- Chen P.H., Chen C.Y., Lin K.C. аt аl. Type IIC Distal Clavicle Fractures with Hook Plates Leads to a High Incidence of Subacromial Osteolysis: A Retrospective Study and Literature Review. Clin Orthop Surg. 2024;16(5):694-701. doi: 10.4055/cios24009.
- Riiser M.O., Molund M. Long-term Functional Outcomes and Complications in Operative Versus Nonoperative Treatment for Displaced Midshaft Clavicle Fractures in Adolescents: A Retrospective Comparative Study. J Pediatr Orthop. 2021;41(5):279-283. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000001768.
- Cole M.W., Collins LK., Familia M.M. et аl. Trends in the Treatment of Adolesc.ent Clavicle Fractures: Are We Listening to the Evidence? J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2023;7(2):22.00277. doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-22-00277.
- Irfan S.A., Ali A.A., Ashkar A. et аl. Predictors requiring special attention to prevent clavicle fracture nonunion: a systematic review of literature. Trauma Surg Acute Care Open. 2023;8(1):001188. doi: 10.1136/tsaco-2023-001188.
- Chechik O., Batash R., Goldstein Y. et al. Surgical approach for open reduction and internal fixation of clavicle fractures: a comparison of vertical and horizontal incisions. International Orthopaedics (SICOT). 2019;43:1977-1982. doi: 10.1007/s00264-018-4139-9.
- Mullis B.H., Jeray K.J., Broderick S. et al. Midshaft clavicle fractures: is anterior plating an acceptable alternative to superior plating? Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2023;33:3373-3377. doi: 10.1007/s00590-023-03563-5.
- Fadi Hammal, Christine Chiu, Janice Y. Kung et al. Pain management for hospitalized patients with rib fractures: A systematic review of randomized clinical trials. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia. 2024;92:111276. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2023.111276.
- eyma Teken, Gzen ksz, Hafize ksz et al. Analgesic efficacy of the serratus anterior plane block in rib fractures pain: A randomized controlled trial. The American Journal of Emergency Medicine. 2021;41:16-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.12.041.
- Erica D. Kane, Elan Jeremitsky, Katharine R. Bittner et al. Surgical Stabilization of Rib Fractures: A Single Institution Experience. Journal of the American College of Surgeons. 2018;226(6):961-966. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2017.11.008.
- Sermonesi G., Bertelli R., Pieracci F.M. et al. Surgical stabilization of rib fractures (SSRF): the WSES and CWIS position paper. World J Emerg Surg. 2024;19(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13017-024-00559-2.
- Eriksson E.A., Wijffels M.M.E., Kaye A. et al. Incidence of surgical rib fixation at chest wall injury society collaborative centers and a guide for expected number of cases (CWIS-CC1). Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2024;50(2):417-423. doi: 10.1007/s00068-023-02343-4.