Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 19, №5, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Неврологічні прояви в дітей з інфекцією COVID-19
Авторы: Ahmed Abdul Hadi Mohsen (1), Alaa Abdul Muslim Kadhim (2), Hiba Sadiq Mohammed Hassan (1), Jasim Mohamed Hashim Al Mosawy (3), Alaa Jumaah Manji Nasrawi (3)
(1) - College of Medicine, Jabir ibn Hayyan Medical University, Najaf, Iraq
(2) - Al Najaf Health Directorate, Najaf, Iraq
(3) - College of Medicine, University of Kufa, Najaf, Iraq
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
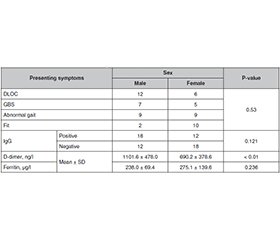
Актуальність. Діти, інфіковані COVID-19, можуть мати різноманітні неврологічні симптоми. Під час спалаху COVID-19 лікарі повинні розглядати інфекцію SARS-CoV-2 як диференційний діагноз при веденні пацієнтів із неврологічними симптомами. Метою цього дослідження є вивчення неврологічних симптомів інфекції COVID-19. Матеріали та методи. Перехресне дослідження включало 100 пацієнтів (віком від 1 місяця до 12 років), які були госпіталізовані до відділення невідкладної допомоги з неврологічними симптомами в період з 1 жовтня 2020 р. до 1 серпня 2021 р. Результати. Шістдесят із 100 пацієнтів мали позитивний результат тестування на COVID-19, що було підтверджено методом полімеразної ланцюгової реакції. У вісімнадцяти (30 %) дітей спостерігалися слабкість нижніх кінцівок і порушення ходи, судоми виявлено в 12 (20 %) випадках, порушення рівня свідомості — у 18 (30 %), синдром, схожий на синдром Гієна — Барре, — у 12 (20 %); майже в усіх пацієнтів результат був сприятливим. Загалом неврологічні прояви були більш поширеними в дітей шкільного віку, ніж в інших вікових групах (p = 0,01). Висновки. Ми представили ці випадки, щоб підкреслити зв’язок між COVID-19 і неврологічними проявами, оскільки виявилося, що, у той час як розлад свідомості є поширеним серед дітей шкільного віку, судоми частіше спостерігаються в немовлят.
Background. Children infected with COVID-19 may experience a variety of neurological symptoms. During the outbreak of COVID-19, doctors should consider SARS-CoV-2 infection as a differential diagnosis when meeting patients with neurological symptoms. This study aims to investigate the neurological symptoms of COVID-19 infection. Materials and methods. A cross-sectional study enrolled 100 patients (age range from 1 month to 12 years) admitted to the emergency room with neurological symptoms between October 1, 2020, and August 1, 2021. Results. Sixty out of 100 patients were positive for COVID-19 that was confirmed by polymerase chain reaction. Eighteen (30 %) children had lower limb weakness and abnormal gait, fit was detected in 12 (20 %) cases, a disturbed level of consciousness — in 18 (30 %), and Guillain-Barre-like syndrome — in 12 (20 %); the outcome was favorable in almost all patients. Overall, neurological manifestations were more common in school-age children than in other age groups (p-value of 0.01). Conclusions. We presented these cases to highlight the link between COVID-19 and neurological manifestations, as it was found that while a disturbed state of consciousness is common among school-age children, convulsions are more common in infancy.
неврологічні прояви; COVID-19; порушений рівень свідомості; порушення ходи; судоми
neurological manifestation; COVID-19; disturbed level of consciousness; abnormal gait; fit
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Mishra A, O’Farrell FM, Reynell C, et al. Imaging pericytes and capillary diameter in brain slices and isolated retinae. Nature Protocols. 2014;9:323-36.
- Mehrabadi ME, Hemmati R, Tashakor A, et al. Induced dysregulation of ACE2 by SARS-CoV-2 plays a key role in COVID-19 severity. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2021;5:111363.
- Consiglio CR, Cotugno N, Sardh F, et al. The immunology of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children with COVID-19. Cell. 2020;183:968-81.
- Iadecola C, Anrather J, Kamel H. Effects of COVID-19 on the nervous system. Cell. 2020.
- Amezcua JM, Jain R, Kleinman G, et al. COVID-19-induced neurovascular injury: a case series with an emphasis on pathophysiological mechanisms. SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine. 2020;22:1-7.
- Schurink B, Roos E, Radonic T, et al. Viral presence and immunopathology in patients with lethal COVID-19: a prospective autopsy cohort study. The Lancet Microbe. 2020;1:e290-9.
- Crippa S, Kägi G, Graf L, Sauteur PM, et al. Stroke in a young adult with mild COVID-19 suggesting endothelins. New Microbes and New Infections. 2020;38:100781.
- Gulko E, Overby P, Ali S, Mehta H, et al. Vessel wall enhancement and focal cerebral arteriopathy in a pediatric patient with acute infarct and COVID-19 infection. American Journal of Neuroradiology. 2020;41:2348-50.
- Ranabothu S, Onteddu S, Nalleballe K, et al. The spectrum of COVID-19 in children. Acta Paediatrica (Oslo, Norway: 1992). 2020.
- Appavu B, Deng D, Dowling MM, et al. Arteritis and large vessel occlusive strokes in children after COVID-19 infection. Pediatrics. 2021;3:147.
- Beslow LA, Linds AB, Fox CK, et al. Pediatric Ischemic Stroke: An Infrequent Complication of SARS-CoV-2. Annals of Neurology. 2021;89:657-65.
- Mirzaee SM, Gonçalve Mohammadifard M, Tavakoli SM, Vossough A. Focal cerebral arteriopathy in a pediatric patient with –COVID-19. Radiology. 2020;297:E274-5.
- Solomon IH, Normandin E, Bhattacharyya S, et al. Neuropathological features of COVID-19. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020;383:989-92.
- Schober ME, Pavia AT, Bohnsack JF. Neurologic manifestations of COVID-19 in children: emerging pathophysiologic insights. Pediatric Critical Care Medicine. 2021;22:655.
- Siracusa L, Cascio A, Giordano S, et al. Neurological complications in pediatric patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a systematic review of the literature. Italian Journal of Pediatrics. 2021;47(1):123.
- Abdel-Mannan O, Eyre M, Löbel U, Bamford A, et al. Neurologic and radiographic findings associated with COVID-19 infection in children. JAMA Neurology. 2020;77:1440-5.
- González-Donapetry P, García-Clemente P, Bloise I, et al. Think of the Children: Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Test in Pediatric Population. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal. 2021;40:385-8.
- Heald-Sargent T, Muller WJ, Zheng X, Rippe J, et al. Age-rela–ted differences in nasopharyngeal severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) levels in patients with mild to moderate coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA Pediatrics. 2020;174:902-3.
- Feldstein LR, Rose EB, Horwitz SM et al. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in US Children and Adolescents. New Engl J Med. 2020;383:334-346.
- Del Borrello G, Giraudo I, Bondone C, et al. SARS-CoV-2-associated coagulopathy and thromboembolism prophylaxis in children: A single-center observational study. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 2021;19:522-30.
- Yildiz E, Cigri E, Dincer Z, Narsat MA, et al. High Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratios in Symptomatic Pediatric COVID-19 Patients. –JCPSP. 2021;31:93-8.