Журнал "Гастроэнтерология" Том 58, №3, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Особливості експресії клаудинів 1 і 7 у слизовій оболонці товстої кишки при симптоматичній неускладненій дивертикулярній хворобі та гострому неускладненому дивертикуліті
Авторы: Дорогавцева Г.А. (1), Дорофєєв А.Е. (2), Дядик О.О. (2), Мирошниченко М.С. (3), Бібіченко В.О. (3)
(1) - Клінічна лікарня «Феофанія» ДУС, м. Київ, Україна
(2) - Національний університет охорони здоров’я України імені П.Л. Шупика, м. Київ, Україна
(3) - Харківський національний медичний університет, м. Харків, Україна
Рубрики: Гастроэнтерология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
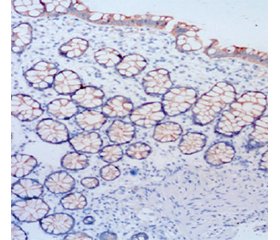
Актуальність. Дивертикулярна хвороба є однією з найпоширеніших патологій шлунково-кишкового тракту, яка переважно ушкоджує товсту кишку і морфологічно маніфестує формуванням кістоподібних випинань (дивертикулів) кишкової стінки. Етіопатогенез дивертикулярної хвороби на сьогодні залишається дискутабельним і не повністю вивченим питанням. Зміни експресії клаудинів у слизовій оболонці товстої кишки та, відповідно, їх структурна нестабільність можуть відігравати певну роль у розвитку як самої дивертикулярної хвороби, так і її ускладнень. Мета: визначити особливості експресії клаудинів 1 і 7 у слизовій оболонці товстої кишки хворих на симптоматичну неускладнену дивертикулярну хворобу (СНДХ) і гострий неускладнений дивертикуліт (ГНД). Матеріали та методи. Матеріалом дослідження були фрагменти слизової оболонки товстої кишки 12 осіб без патології шлунково-кишкового тракту (група 1), біоптати слизової оболонки товстої кишки з зони устя дивертикулу 34 хворих на СНДХ (група 2) і 26 хворих на ГНД (група 3). Проведено імуногістохімічне дослідження з використанням кролячих поліклональних антитіл до клаудинів 1 і 7. Одержані цифрові показники в групах обробляли статистично за допомогою програми PAST. Середні значення показників у групах порівнювали за допомогою t-критерію Стьюдента, U-критерію Манна — Уїтні. Результати. Комплексне морфологічне дослідження виявило зниження експресії клаудинів 1 і 7 у слизовій оболонці товстої кишки хворих на СНДХ і ГНД, що було максимально вираженим у випадках ГНД. У хворих на СНДХ і ГНД, як і в осіб без патології шлунково-кишкового тракту, у слизовій оболонці товстої кишки, по-перше, вміст клаудинів 1 і 7 був більшим у поверхневому епітелії порівняно з епітелієм кишкових залоз, по-друге, вміст клаудину 1 превалював над вмістом клаудину 7. Висновки. Виявлені авторами зміни експресії клаудинів 1 і 7 у біоптатах слизової оболонки товстої кишки можуть лежати в основі розвитку як самої дивертикулярної хвороби, так і її ускладнень.
Background. Diverticular disease is one of the most common gastrointestinal pathologies, which mainly damages the large intestine and is manifested morphologically by the formation of sac-like protrusions (diverticula) of the intestinal wall. Today, the etiopathogenesis of diverticular disease remains debatable and needs to be fully understood. Changes in the claudin expression in the colonic mucosa and, accordingly, their structural instability may play a certain role in the development of both diverticular disease and its complications. The study aimed to determine the features of claudin 1 and 7 expression in the colonic mucosa of patients with symptomatic uncomplicated diverticular disease (SUDD) and acute uncomplicated diverticulitis (AUD). Materials and methods. Fragments of the colonic mucosa of 12 individuals without gastrointestinal pathology (group 1), biopsies of the colonic mucosa from the diverticular orifice of 34 patients with SUDD (group 2) and 26 patients with AUD (group 3) were analyzed. An immunohistochemical study used rabbit polyclonal antibodies to claudins 1 and 7. The PAST program was applied to process digital indicators. The average indicators in groups were compared using the Student’s t-test and Mann-Whitney U-test. Results. A comprehensive morphological study revealed a decrease in the expression of claudins 1 and 7 in the colonic mucosa of patients with SUDD and AUD, more pronounced in those with AUD. In the large intestine mucosa of people without gastrointestinal pathology and patients with SUDD and AUD, firstly, the content of claudins 1 and 7 was higher in the surface epithelium compared to the epithelium of the intestinal glands, secondly, the content of claudin 1 predominated over claudin 7 content. Conclusions. The detected changes in claudin 1 and 7 expression in the colonic mucosa biopsies may underlie the development of diverticular disease and its complications.
клаудини 1 і 7; слизова оболонка товстої кишки; особливості експресії клаудинів 1 і 7; симптоматична неускладнена дивертикулярна хвороба; гострий неускладнений дивертикуліт
claudins 1 and 7; mucous membrane of the large intestine; features of claudin 1 and 7 expression; symptomatic uncomplicated diverticular disease; acute uncomplicated diverticulitis
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Song C, Chai Z, Chen S, Zhang H, Zhang X, Zhou Y. Intestinal mucus components and secretion mechanisms: what we do and do not know. Exp Mol Med. 2023 Apr;55(4):681-691. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-00960-y. Epub 2023 Apr 3. PMID: 37009791; PMCID: PMC10167328.
- Vancamelbeke M, Vermeire S. The intestinal barrier: a fundamental role in health and disease. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Sep;11(9):821-834. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2017.1343143. Epub 2017 Jun 26. PMID: 28650209; PMCID: PMC6104804.
- Hladky O. Epithelial barrier and probiotics: how to build a wall at the border with diseases. Health of Ukraine. 2023;18(554):40-41. Ukrainian.
- Denisova MF, Zadorojna TD, Bukulova NY, Archakova TM. Colon epithelial barrier state in children with varios types of ulcerative colitis clinical forms. Ukrainian Journal of Perinatology and Pediatrics. 2021;1(85):53-61. doi: 10.15574/PP.2021.85.53. Ukrainian.
- Myroshnychenko MS, Torianyk II, Arseniev OV, Franchuk VV, Zaytseva OV, Moiseienko TM et al. Morphological and functional features of the mucous membrane of small and large intestine in patients with COVID-19 and in post-COVID-19 period. Wiad Lek. 2022;75(9 pt 2):2198-2203. doi: 10.36740/WLek202209203. PMID: 36378694.
- Griffiths V, Al Assaf N, Khan R. Review of claudin proteins as potential biomarkers for necrotizing enterocolitis. Ir J Med Sci. 2021 Nov;190(4):1465-1472. doi: 10.1007/s11845-020-02490-2. Epub 2021 Jan 25. PMID: 33492576; PMCID: PMC8521514.
- Abaturov OE, Lykova AE. Chronic Helicobacter pylori-associated infection in children, paracellular permeability of the gastric mucosa and food allergy. Child’s Health. 2019;14(1):44-49. doi: 10.22141/2224-0551.14.1.2019.157879. Ukrainian.
- Kozieł MJ, Ziaja M, Piastowska-Ciesielska AW. Intestinal Barrier, Claudins and Mycotoxins. Toxins (Basel). 2021 Oct 26;13(11):758. doi: 10.3390/toxins13110758. PMID: 34822542; PMCID: PMC8622050.
- Garcia-Hernandez V, Quiros M, Nusrat A. Intestinal epithelial claudins: expression and regulation in homeostasis and inflammation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017 Jun;1397(1):66-79. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13360. Epub 2017 May 10. PMID: 28493289; PMCID: PMC5545801.
- Kim DY, Furuta GT, Nguyen N, Inage E, Masterson JC. Epithelial Claudin Proteins and Their Role in Gastrointestinal Diseases. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2019 May;68(5):611-614. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000002301. PMID: 30724794; PMCID: PMC6483856.
- Piscopo N, Ellul P. Diverticular Disease: A Review on Pathophysiology and Recent Evidence. Ulster Med J. 2020 Sep;89(2):83-88. Epub 2020 Oct 21. PMID: 33093692; PMCID: PMC7576390.
- Barbaro MR, Cremon C, Fuschi D, Marasco G, Palombo M, Stanghellini V, Barbara G. Pathophysiology of Diverticular Disease: From Diverticula Formation to Symptom Generation. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 15;23(12):6698. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126698. PMID: 35743141; PMCID: PMC9223421.
- Ivanova M, Myroshnychenko M, Khara G, Arseniev O, Olkhovsky V, Grygorian E, Fedulenkova Y, Kozlov S. Analysis of color properties of raster images of histological microspecimens: own research experience. Med. perspekt. [Internet]. 2022 Mar 30;27(1):9-15. https://journals.uran.ua/index.php/2307-0404/article/view/254314.
- Ding Y, Wang K, Xu C, Hao M, Li H, Ding L. Intestinal Claudin-7 deficiency impacts the intestinal microbiota in mice with colitis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Jan 17;22(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02100-8. PMID: 35039003; PMCID: PMC8762895.
- Paradis T, Bègue H, Basmaciyan L, Dalle F, Bon F. Tight Junctions as a Key for Pathogens Invasion in Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 2;22(5):2506. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052506. PMID: 33801524; PMCID: PMC7958858.
- Zhu L, Han J, Li L, Wang Y, Li Y, Zhang S. Claudin Fami–ly Participates in the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer. Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 27;10:1441. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01441. PMID: 31316506; PMCID: PMC6610251.
- Dorofeyev AE, Tkach SM, Dyadyk ОО, Prikhodko VM. Features of the mucous barrier in functional bowel diseases and ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 2022. 2022;56(2):32-37. Ukrainian.
- Tursi A, Elisei W. Role of Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Diverticular Disease. Mediators Inflamm. 2019 Mar 14;2019:8328490. doi: 10.1155/2019/8328490. PMID: 31001067; PMCID: PMC6437747.
- Altomare A, Gori M, Cocca S, Carotti S, Francesconi M, Ribolsi M et al. Impaired Colonic Contractility and Intestinal Permeability in Symptomatic Uncomplicated Diverticular Disease. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021 Apr 30;27(2):292-301. doi: 10.5056/jnm20110. PMID: 33594008; PMCID: PMC8026365.
- Scaioli E, Colecchia A, Marasco G, Schiumerini R, Festi D. Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Strategies for Symptomatic Uncomplicated Diverticular Disease of the Colon. Dig Dis Sci. 2016 Mar;61(3):673-83. doi: 10.1007/s10620-015-3925-0. Epub 2015 Oct 12. PMID: 26458921.
- Calini G, Abd El Aziz MA, Paolini L, Abdalla S, Rottoli M, Mari G, Larson DW. Symptomatic Uncomplicated Diverticular Disease (SUDD): Practical Guidance and Challenges for Clinical Management. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2023 Mar 28;16:29-43. doi: 10.2147/CEG.S340929. PMID: 37013200; PMCID: PMC10066719.