Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 19, №3, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Бемпедоєва кислота: механізм дії та застосування при атеросклеротичних серцево-судинних захворюваннях і цукровому діабеті
Авторы: Сергієнко В.О., Сергієнко О.О.
Львівський національний медичний університет імені Данила Галицького, м. Львів, Україна
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
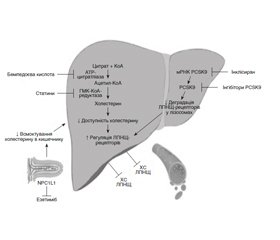
Бемпедоєва кислота — новий лікарський засіб (ЛЗ) для зниження рівня холестерину, який нещодавно отримав схвалення Управління з контролю за продуктами й ліками США та Європейського агентства з лікарських засобів. Цей ЛЗ націлений на метаболізм ліпідів і глюкози, а також на запалення шляхом зниження регуляції аденозинтрифосфатцитратліази та підвищення регуляції аденозинмонофосфат-активованої протеїнкінази (AMPK). Основним ефектом є зниження синтезу холестерину в печінці, і його використання, як правило, не пов’язане з небажаними м’язовими розладами. Бемпедоєва кислота може зменшувати процеси глюконеогенезу, що призводить до покращення чутливості до інсуліну, метаболізму глюкози й особливостей перебігу метаболічного синдрому. Протизапальна дія бемпедоєвої кислоти переважно досягається шляхом активації шляху AMPK в імунних клітинах, що сприяє зниженню рівня С-реактивного білка в плазмі. Вплив бемпедоєвої кислоти на перебіг атеросклеротичних серцево-судинних захворювань, цукрового діабету 2-го типу і хронічних захворювань печінки оцінювали в рандомізованих клінічних дослідженнях, які потребують проведення подальших випробувань. Клінічні дослідження безпеки у фазі III показують, що бемпедоєва кислота загалом добре переноситься в комбінації зі статинами, езетимібом або інгібіторами пропротеїнової конвертази субтилізин/кексин типу 9 для досягнення цільових показників холестерину ліпопротеїнів низької щільності. Метою цього огляду є аналіз основних механізмів дії, потенційних клінічних цілей бемпедоєвої кислоти та опис існуючих доказів клінічних випробувань. Пошук проводився в Scopus, Science Direct (від Elsevier) і PubMed, включно з базами даних Medline. Використані ключові слова «бемпедоєва кислота», «холестерин ліпопротеїнів низької щільності», «атеросклеротичні серцево-судинні захворювання», «цукровий діабет». Для виявлення результатів дослідження, які не вдалося знайти під час онлайн-пошуку, використовувався ручний пошук бібліографії публікацій.
Bempedoic acid is a new cholesterol-lowering drug that recently received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration and the European Medicines Agency. This drug targets lipid and glucose metabolism as well as inflammation by downregulating the ATP citrate lyase and upregulating of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). The main effect is to reduce cholesterol synthesis in the liver, and its use is generally not associated with undesirable muscle disorders. Bempedoic acid can reduce the processes of gluconeogenesis, which leads to an improvement in insulin sensitivity, glucose metabolism and features of the metabolic syndrome. The anti-inflammatory effect of bempedoic acid is mainly achieved by activating the AMPK pathway in immune cells, which helps reduce the level of C-reactive protein in plasma. The effects of bempedoic acid on the course of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes and chronic liver disease have been evaluated in randomized clinical trials that require further research. Phase III clinical safety trial show that bempedoic acid is generally well tolerated in combination with statins, ezetimibe, or proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors in achieving target levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. The aim of this review is to analyze the main mechanisms of action, potential clinical targets of bempedoic acid and describe the existing evidence from clinical trials. The search was done in the Scopus, Science Direct (from Elsevier), and PubMed databases, including the Medline. The following keywords were used: bempedoic acid, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases, diabetes. In order to identify research results that could not be found during the online search, a manual search of the bibliography of publications was used.
бемпедоєва кислота; холестерин ліпопротеїнів низької щільності; атеросклеротичні серцево-судинні захворювання; цукровий діабет 2-го типу; огляд
bempedoic acid; low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases; type 2 diabetes; review
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Visseren F.L.J., Mach F., Smulders Y.M., Carballo D., Koskinas K.C., Bäck M., Benetos A. et al.; ESC National Cardiac Societies; ESC Scientific Document Group. 2021 ESC Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice. Eur. Heart J. 2021. Sep 7. 42(34). 3227-3337. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab484.
- Pearson G.J., Thanassoulis G., Anderson T.J., Barry A.R., Couture P., Dayan N., Francis G.A. et al. 2021 Canadian Cardiovascular Society Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidemia for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in Adults. Can. J. Cardiol. 2021. Aug. 37(8). 1129-1150. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2021.03.016.
- Joseph J.J., Deedwania P., Acharya T., Aguilar D., Bhatt D.L., Chyun D.A., Di Palo K.E. et al.; American Heart Association Diabetes Committee of the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health; Council on Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology; Counсil on Clinical Cardiology; and Council on Hypertension. Comprehensive Mana–gement of Cardiovascular Risk Factors for Adults With Type 2 Diabetes: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2022. Mar. 145(9). e722-e759. doi: 10.1161/ CIR.0000000000001040.
- Ballantyne C.M., Laufs U., Ray K.K., Leiter L.A., Bays H.E., Goldberg A.C. et al. Bempedoic acid plus ezetimibe fixed-dose combination in patients with hypercholesterolemia and high CVD risk treated with maximally tolerated statin therapy. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020. Apr. 27(6). 593-603. doi: 10.1177/2047487319864671.
- ElSayed N.A., Aleppo G., Aroda V.R., Bannuru R.R., Brown F.M., Bruemmer D., Collins B.S. et al., on behalf of the American Diabetes Association. 10. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Mana–gement: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care. 2023. Jan 1. 46 (Suppl. 1). S158-S190. doi: 10.2337/dc23-S010.
- Serhiyenko V.A., Serhiyenko A.A. Diabetic cardiac autonomic neuropathy. In: Saldaña J.R., ed. Diabetes Textbook: Clinical Principles, Patient Management and Public Health Issues. Basel: Springer, Cham. Springer Nature Switzerland AG. 2019. 825-850. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-11815-0_53.
- Di Minno A., Lupoli R., Calcaterra I., Poggio P., Forte F., Spadarella G., Ambrosino P. et al. Efficacy and Safety of Bempedoic Acid in Patients With Hypercholesterolemia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020. Aug 4. 9(15). e016262. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.016262.
- Govindaraju A., Sabarathinam S. Bempedoic acid: A nonstatin drug for the management of hypercholesterolemia. Health Sci. Rep. 2021. Nov 9. 4(4). e431. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.431.
- Bardolia C., Amin N.S., Turgeon J. Emerging Non-statin Treatment Options for Lowering Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021. Nov 17. 8. 789931. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.
- Ziegler D., Porta M., Papanas N., Mota M., Jermendy G., Beltramo E., Mazzeo A. et al. The role of biofactors in diabetic microvascular complications. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2022. 18(4). e250821195830. doi: 10.2174/1871527320666210825112240.
- Dai L., Zuo Y., You Q., Zeng H., Cao S. Efficacy and safety of bempedoic acid in patients with hypercholesterolemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2021. Jul 23. 28(8). 825-833. doi: 10.1177/2047487320930585.
- Tummala R., Gupta M., Devanabanda A.R., Bandyopadhyay D., Aronow W.S., Ray K.K. et al. Bempedoic acid and its role in contemporary management of hyperlipidemia in atherosclerosis. Ann. Med. 2022. Dec. 54(1). 1287-1296. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2059559.
- Santangelo G., Moscardelli S., Simeoli P.S., Guazzi M., Faggiano P. Management of Dyslipidemia in Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: The Gap between Theory and Practice. J. Clin. Med. 2022. Aug 8. 11(15). 4608. doi: 10.3390/jcm11154608.
- Serhiyenko V., Serhiyenko A. Ezetimibe and diabetes mellitus: A new strategy for lowering cholesterol. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2022. 18(5). 302-314. doi:10.22141/2224-0721.18.5.2022.1190.
- Gutierrez M.J., Rosenberg N.L., Macdougall D.E., Hanselman J.C., Margulies J.R., Strange P., Milad M.A. et al. Efficacy and safety of ETC-1002, a novel investigational low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol-lowering therapy for the treatment of patients with hypercholesterolemia and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014. Mar. 34(3). 676-683. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302677.
- Thompson P.D., Rubino J., Janik M.J., MacDougall D.E., McBride S.J., Margulies J.R., Newton R.S. Use of ETC-1002 to treat hypercholesterolemia in patients with statin intolerance. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2015. May-Jun. 9(3). 295-304. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2015.03.003.
- Thompson P.D., MacDougall D.E., Newton R.S., Margulies J.R., Hanselman J.C., Orloff D.G., McKenney J.M. et al. Treatment with ETC-1002 alone and in combination with ezetimibe lowers LDL cholesterol in hypercholesterolemic patients with or without statin intolerance. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2016. May-Jun. 10(3). 556-567. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2015.12.025.
- Authors/Task Force Members, ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines (CPG), ESC National Cardiac Societies. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Atherosclerosis. 2019. 290. 140-205. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.08.014.
- Lalwani N.D., Hanselman J.C., MacDougall D.E., Sterling L.R., Cramer C.T. Complementary low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol lowering and pharmacokinetics of adding bempedoic acid (ETC-1002) to high-dose atorvastatin background therapy in hypercholesterolemic patients: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2019. 13(4). 568-579. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2019.05.003.
- Mach F., Baigent C., Catapano A.L., Koskinas K.C., Casula M., Badimon L., Chapman M.J. et al.; ESC Scientific Document Group. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur. Heart J. 2020. Jan 1. 41(1). 111-188. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz455.
- Rubino J., MacDougall D.E., Sterling L.R., Hanselman J.C., Nicholls S.J. Combination of bempedoic acid, ezetimibe, and atorvastatin in patients with hypercholesterolemia: A randomized clinical trial. Atherosclerosis. 2021. Mar. 320. 122-128. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2020.12.023.
- Biolo G., Vinci P., Mangogna A., Landolfo M., Schinca–riol P., Fiotti N., Mearelli F. et al. Mechanism of action and therapeutic use of bempedoic acid in atherosclerosis and metabolic syndrome. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022. Oct 28. 9. 1028355. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1028355.
- Markham A. Bempedoic Acid: First Approval. Drugs. 2020 May. 80(7). 747-753. doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01308-w.
- Alam U., Al-Bazz D.Y., Soran H. Bempedoic Acid: The New Kid on the Block for the Treatment of Dyslipidemia and LDL Cholesterol: A Narrative Review. Diabetes Ther. 2021. Jul. 12(7). 1779-1789. doi: 10.1007/s13300-021-01070-6.
- Pinkosky S.L., Filippov S., Srivastava R.A., Hanselman J.C., Bradshaw C.D., Hurley T.R., Cramer C.T. et al. AMP-activated protein kinase and ATP-citrate lyase are two distinct molecular targets for ETC-1002, a novel small molecule regulator of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013. Jan. 54(1). 134-151. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M030528.
- Pinkosky S.L., Newton R.S., Day E.A., Ford R.J., Lhotak S., Austin R.C., Birch C.M. et al. Liver-specific ATP-citrate lyase inhibition by bempedoic acid decreases LDL-C and attenuates atherosclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2016. Nov 28. 7. 13457. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13457.
- Burke A.C., Telford D.E., Huff M.W. Bempedoic acid: effects on lipoprotein metabolism and atherosclerosis. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2019. Feb. 30(1). 1-9. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000565.
- Samsoondar J.P., Burke A.C., Sutherland B.G., Telford D.E., Sawyez C.G., Edwards J.Y., Pinkosky S.L. et al. Prevention of Diet-Induced Metabolic Dysregulation, Inflammation, and Atherosclerosis in Ldlr-/- Mice by Treatment With the ATP-Citrate Lyase Inhibitor Bempedoic Acid. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017. Apr. 37(4). 647-656. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308963.
- Filippov S., Pinkosky S.L., Lister R.J., Pawloski C., Hanselman J.C., Cramer C.T., Srivastava R.A.K. et al. ETC-1002 regulates immune response, leukocyte homing, and adipose tissue inflammation via LKB1-dependent activation of macrophage AMPK. J. Lipid Res. 2013. Aug. 54(8). 2095-2108. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M035212.
- Verberk S.G.S., Kuiper K.L., Lauterbach M.A., Latz E., Van den Bossche J. The multifaceted therapeutic value of targeting ATP-citrate lyase in atherosclerosis. Trends Mol. Med. 2021. Dec. 27(12). 1095-1105. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2021.09.004.
- Ference B.A., Robinson J.G., Brook R.D., Catapano A.L., Chapman M.J., Neff D.R. et al. Variation in PCSK9 and HMGCR and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016. Dec 1. 375(22). 2144-2153. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1604304.
- Ference B.A., Ray K.K., Catapano A.L., Ference T.B., Burgess S., Neff D.R. et al. Mendelian Randomization Study of ACLY and Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019. Mar 14. 380(11). 1033-1042. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1806747.
- Morrow M.R., Batchuluun B., Wu J., Ahmadi E., Le–roux J.M., Mohammadi-Shemirani P., Desjardins E.M. et al. Inhibition of ATP-citrate lyase improves NASH, liver fibrosis, and dyslipidemia. Cell Metab. 2022. Jun 7. 34(6). 919-936.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.05.004.
- Bouchard-Mercier A., Rudkowska I., Lemieux S., Couture P., Vohl M.C. Polymorphisms, de novo lipogenesis, and plasma triglyceride response following fish oil supplementation. J. Lipid Res. 2013. Oct. 54(10). 2866-2873. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M041590.
- Rubino J., MacDougall D.E., Sterling L.R., Kelly S.E., Mc–Kenney J.M., Lalwani N.D. Lipid lowering with bempedoic acid added to a proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor therapy: A randomized, controlled trial. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2021. Jul-Aug. 5(4). 593-601. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2021.05.002.
- Cicero A.F.G., Fogacci F., Hernandez A.V., Banach M.; Lipid and Blood Pressure Meta-Analysis Collaboration (LBPMC) Group and the International Lipid Expert Panel (ILEP). Efficacy and safety of bempedoic acid for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 2020. 17(7). e1003121. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003121.
- Ballantyne C.M., McKenney J.M., MacDougall D.E., Margulies J.R., Robinson P.L., Hanselman J.C., Lalwani N.D. Effect of ETC-1002 on Serum Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Hypercholesterolemic Patients Receiving Statin Therapy. Am. J. Cardiol. 2016. Jun 15. 117(12). 1928-1933. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2016.03.043.
- Ray K.K., Del Prato S., Müller-Wieland D., Cariou B., Colhoun H.M., Tinahones F.J., Domenger C. et al. Alirocumab therapy in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: analysis of the ODYSSEY DM-DYSLIPIDEMIA and DM-INSULIN studies. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019. Nov 9. 18(1). 149. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0951-9.
- Goldberg A.C., Leiter L.A., Stroes E.S.G., Baum S.J., Hanselman J.C., Bloedon L.T., Lalwani N.D. et al. Effect of Bempedoic Acid vs Placebo Added to Maximally Tolerated Statins on Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Patients at High Risk for Cardiovascular Disease: The CLEAR Wisdom Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2019 Nov 12. 322(18). 1780-1788. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.16585.
- Laufs U., Banach M., Mancini G.B.J., Gaudet D., Bloedon L.T., Sterling L.R., Kelly S. et al. ESG. Efficacy and Safety of Bempedoic Acid in Patients With Hypercholesterolemia and Statin Intolerance. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019. Apr 2. 8(7). e011662. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.011662.
- Bays H.E., Banach M., Catapano A.L., Duell P.B., Gotto A.M. Jr., Laufs U., Leiter L.A. et al. Bempedoic acid safety analysis: Pooled data from four phase 3 clinical trials. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2020. Sep-Oct. 14(5). 649-659. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2020.08.009.
- Ballantyne C.M., Banach M., Mancini G.B.J., Lepor N.E., Hanselman J.C., Zhao X., Leiter L.A. Efficacy and safety of bempedoic acid added to ezetimibe in statin-intolerant patients with hypercholesterolemia: A randomized, placebo-controlled study. Atherosclerosis. 2018. Oct. 277. 195-203. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.06.002.
- Pirillo A., Catapano A.L. New insights into the role of bempedoic acid and ezetimibe in the treatment of hypercholesterolemia. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2022. Apr 1. 29(2). 161-166. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000706.
- Cicero A.F.G., Pontremoli R., Fogacci F., Viazzi F., Borghi C. Effect of Bempedoic Acid on Serum Uric Acid and Related Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of the available Phase 2 and Phase 3 Clinical Studies. Drug Saf. 2020. Aug. 43(8). 727-736. doi: 10.1007/s40264-020-00931-6.
- Ray K.K., Bays H.E., Catapano A.L., Lalwani N.D., Bloedon L.T., Sterling L.R. et al.; CLEAR Harmony Trial. Safety and Efficacy of Bempedoic Acid to Reduce LDL Cholesterol. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019. Mar 14. 380(11). 1022-1032. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1803917.
- Wang X., Zhang Y., Tan H., Wang P., Zha X., Chong W. et al. Efficacy and safety of bempedoic acid for prevention of cardiovascular events and diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020. Aug 12. 19(1). 128. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01101-9.
- Lin Y., Parco C., Karathanos A., Krieger T., Schulze V., Chernyak N., Icks A. et al. Clinical efficacy and safety outcomes of bempedoic acid for LDL-C lowering therapy in patients at high cardiovascular risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. B.M.J. Open. 2022. Feb 24. 12(2). e048893. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-048893.
- Masson W., Barbagelata L., Lobo M., Nogueira J.P. Bempedoic acid in patients with type 2 diabetes. Rev. Clin. Esp. (Barc.). 2022. Apr. 222(4). 251-253. doi: 10.1016/j.rceng.2021.11.003.
- Leiter L.A., Banach M., Catapano A.L., Duell P.B., Gotto A.M. Jr., Laufs U., Mancini G.B.J. et al. Bempedoic acid in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, prediabetes, and normoglycaemia: A post hoc analysis of efficacy and glycaemic control using pooled data from phase 3 clinical trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022. May. 24(5). 868-880. doi: 10.1111/dom.14645.
- Honigberg M.C., Natarajan P. Bempedoic Acid for Lowering LDL Cholesterol. JAMA. 2019. Nov 12. 322(18). 1769-1771. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.16598.
- Ruscica M., Banach M., Sahebkar A., Corsini A., Sirtori C.R. ETC-1002 (Bempedoic acid) for the management of hyperlipidemia: from preclinical studies to phase 3 trials. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2019. May. 20(7). 791-803. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2019.1583209.
- Koval S.M., Yushko K.O., Snihurska I.O., Starchenko T.G., Pankiv V.I., Lytvynova O.M., Mysnychenko O.V. Relations of angiotensin-(1-7) with hemodynamic and cardiac structural and functional parameters in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Arterial Hypertension. 2019. 23(3). 183-189. DOI: 10.5603/AH.a2019.0012.
- Gupta M., Tummala R., Ghosh R.K., Blumenthal C., Phi–lip K., Bandyopadhyay D. et al. An update on pharmacotherapies in diabetic dyslipidemia. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019. Jul-Aug. 62(4). 334-341. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2019.07.006.
- Niman S., Rana K., Reid J., Sheikh-Ali M., Lewis T., Choksi R.R., Goldfaden R.F. A Review of the Efficacy and Tolerability of Bempedoic Acid in the Treatment of Hypercholesterolemia. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs. 2020. Dec. 20(6). 535-548. doi: 10.1007/s40256-020-00399-w.
- Caselli C., Del Turco S., Ragusa R., Lorenzoni V., De Graaf M., Basta G., Scholte A. et al. Association of PCSK9 plasma levels with metabolic patterns and coronary atherosclerosis in patients with stable angina. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019. Oct 31. 18(1). 144. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0949-3.
- O’Mahoney L.L., Matu J., Price O.J., Birch K.M., Ajjan R.A., Farrar D., Tapp R. et al. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids favourably modulate cardiometabolic biomarkers in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis and meta-regression of randomized controlled trials. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018. Jul 7. 17(1). 98. doi: 10.1186/s12933-018-0740-x.
- Sheikh O., Vande Hei A.G., Battisha A., Hammad T., Pham S., Chilton R. Cardiovascular, electrophysiologic, and hematologic effects of omega-3 fatty acids beyond reducing hypertriglyceridemia: as it pertains to the recently published REDUCE-IT trial. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019. Jun 24. 18(1). 84. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0887-0.
- Peiró C., Lorenzo Ó., Carraro R., Sánchez-Ferrer C.F. IL-1β Inhibition in Cardiovascular Complications Associated to Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Pharmacol. 2017. Jun 13. 8. 363. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00363.
- Nicholls S., Lincoff A.M., Bays H.E., Cho L., Grobbee D.E., Kastelein J.J., et al. Rationale and design of the CLEAR-outcomes trial: Evaluating the effect of bempedoic acid on cardiovascular events in patients with statin intolerance. Am. Heart J. 2021. May. 235. 104-112. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2020.10.060.
- CLEAR Cardiovascular Outcomes Trial Results. https://www.esperion.com/news-releases/news-release-details/esperion-announ–ces-clear-cardiovascular-outcomes-trial-nexletolr. Accessed: February 28, 2023.
- Nissen S.E., Lincoff A.M., Brennan D., Ray K.K., Mason D., Kastelein J.J.P. et al.; CLEAR Outcomes Investigators. Bempedoic Acid and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Statin-Intolerant Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023. Mar 4. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2215024.