Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 18, №1, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Комплексна оцінка деяких параметрів фагоцитозу у дітей віком 2–5 років залежно від частоти захворюваності на гострі респіраторні інфекції
Авторы: Тимошина О.В., Овчаренко Л.С., Вертегел А.О., Самохін І.В., Кряжев О.В.
Державний заклад «Запорізька медична академія післядипломної освіти МОЗ України», м. Запоріжжя, Україна
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
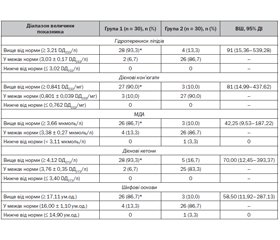
Актуальність. Після зараження респіраторними вірусами спостерігається підвищена продукція прозапальних цитокінів, включно з фактором некрозу пухлини α (ФНП-α), інтерлейкіном (IL) 6, IL-1β, які призводять до перехресної активації нейроендокринної імунної системи, що здатно погіршувати фагоцитоз з підвищенням захворюваності на гострі респіраторні захворювання (ГРЗ), формуючи порочне коло. Мета дослідження: підвищення ефективності діагностики імунних порушень при частих ГРЗ у дітей віком 2–5 років шляхом порівняльного аналізу даних, отриманих на підставі дослідження деяких параметрів фагоцитозу, сироваткових рівнів прозапальних цитокінів та продуктів перекисного окиснення ліпідів (ПОЛ). Матеріали та методи. Під спостереженням перебували 60 дітей віком від 2 до 5 років, з яких було сформовано 2 групи: 1) діти, які часто хворіють на гострі інфекційні захворювання респіраторного тракту (n = 30); 2) діти, які хворіють на гострі інфекційні захворювання респіраторного тракту менше ніж 6 разів на рік (n = 30). Результати. Серед дітей 1-ї групи була збільшена частота реєстрації низьких показників фагоцитарного числа (на 60,0 %, р < 0,05), фагоцитарного індексу (на 56,0 %, р < 0,05), індексу завершеності фагоцитозу (на 70,0 %, р < 0,05), стимульованого стафілококом НСТ-тесту (на 50,0 %, р < 0,05) та високих показників спонтанного НСТ-тесту (на 43,3 %, р < 0,05), вмісту у сироватці крові інтерлейкіну-1β (на 46,7 %, р < 0,05), інтерлейкіну-6 (на 43,3 %, р < 0,05), інтерлейкіну-10 (на 30,0 %, р < 0,05), ФНП-α (на 46,7 %, р < 0,05); відзначалося збільшення співвідношення інтерлейкіну-6/-10 в 2 та більше рази, високих показників гідроперекисів ліпідів (на 80,0 %, р < 0,05), дієнових кон’югат (на 80,0 %, р < 0,05), малонового діальдегіду (на 76,7 %, р < 0,05), дієнових кетонів (на 76,7 %, р < 0,05), шифових основ (на 76,7 %, р < 0,05). Висновки. Діти віком 2–5 років, які часто хворіють на ГРЗ, мають особливості поглинальної, цитокініндукуючої й метаболічної функцій фагоцитозу, що проявилося у збільшенні сироваткової концентрації прозапальних цитокінів та продуктів усіх стадій перекисного окиснення ліпідів клітинних мембран.
Background. After respiratory virus infection, there is an increased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α, interleukin (IL) 6, IL-1β that leads to cross-activation of the neuroendocrine immune system, which can impair phagocytosis with an increase in the incidence of upper respiratory tract infections (URTI), forming a vicious circle. The aim: to increase the effectiveness of diagnosing immune disorders in children aged 2–5 years with recurrent URTI by means of a comparative analysis of data obtained based on the study of some parameters of phagocytosis, serum levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and lipid peroxidation products. Materials and methods. Sixty children aged from 2 to 5 years were under observation, two groups were formed: 1) patients with recurrent URTI (n = 30); 2) children who suffer from URTI less than 6 times a year (n = 30). Results. The children of group 1 had increased frequency of registration of low indicators of the phagocytic number (by 60.0 %, p < 0.05), phagocytic index (by 56.0 %, p < 0.05), and the index of completion of phagocytosis (by 70.0 %, p < 0.05), Staphylococcus-stimulated nitroblue tetrazolium test (by 50.0 %, p < 0.05) and high indicators of spontaneous nitroblue tetrazolium test (by 43.3 %, p < 0.05), high serum levels of IL-1β (by 46.7 %, p < 0.05), IL-6 (by 43.3 %, p < 0.05), IL-10 (by 30.0 %, p < 0.05), TNF-α (by 46.7 %, p < 0.05), an increase in the ratio of IL-6/IL-10 by 2 or more times, high levels of lipid hydroperoxides (by 80.0 %, p < 0.05), diene conjugates (by 80.0 %, p < 0.05), malondialdehyde (by 76.7 %, p < 0.05), diene ketones (by 76.7 %, p < 0.05), Schiff bases (by 76.7 %, p < 0.05). Conclusions. Children aged 2–5 years with recurrent URTI have features of absorptive, cytokine-inducing and metabolic functions of phagocytosis, which was manifested in an increase in the serum concentration of pro-inflammatory cytokines and products of all stages of lipid peroxidation of cell membranes.
діти; фагоцитоз; цитокіни; пероксидація; імунітет
children; phagocytosis; cytokines; peroxidation; immunity
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Jaumouillé V., Waterman C.M. Physical constraints and forces involved in phagocytosis. Frontiers in Immunology. 2020. 11. 1097. doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.01097.
- Hallett M.B. Molecular and Cellular Biology of Phagocytosis. Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2020. 189 p. doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-40406-2.
- Minasyan H. Phagocytosis and oxycytosis: two arms of human innate immunity. Immunologic Research. 2018. 66(2). 271-280. doi.org/10.1007/s12026-018-8988-5.
- Hosakote Y.M., Rayavara K. Respiratory syncytial virus-induced oxidative stress in lung pathogenesis. Oxidative Stress іn Lung Diseases. 2020. 297-330. doi: 10.1007/978-981-32-9366-3_13.
- Leandro C.G., Ferreira E., Silva W.T., Lima-Silva A.E. Covid-19 and Exercise-Induced Immunomodulation. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2020. 27(1). 75-78. doi: 10.1159/000508951.
- Cuppari C., Colavita L., Miraglia Del Giudice M., Chimenz R., Salpietro C. Recurrent respiratory infections between immunity and atopy. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology. 2020. 31. 19-21. doi.org/10.1111/pai.13160.
- Uribe-Querol E., Rosales C. Phagocytosis: our current understanding of a universal biological process. Frontiers in Іmmunology. 2020. 1. 1066. doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.01066.
- Kumar V. Phagocytosis: Phenotypically Simple Yet a Mechanistically Complex Process: Phagocytosis is a very complex but crucial process playing a pivotal role in embryonic development and host defense to maintain immune homeostasis. International Reviews of Immunology. 2020. 39(3). 118-150. doi.org/10.1080/08830185.2020.1732958.
- Xu J., Gong Y., Sun Y., Cai J., Liu Q., Bao J. et al. Impact of selenium deficiency on inflammation, oxidative stress, and phagocytosis in mouse macrophages. Biological Trace Element Research. 2020. 194(1). 237-243. doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01775-7.
- El Euony O.I., Elblehi S.S., Abdel-Latif H.M., Abdel-Daim M.M., El-Sayed Y.S. Modulatory role of dietary Thymus vulgaris essential oil and Bacillus subtilis against thiamethoxam-induced hepatorenal damage, oxidative stress, and immunotoxicity in African catfish (Clarias garipenus). Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 2020. 27(18). 23108-23128. doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08588-5.
- Liu J., Chen X., Qiu X., Zhang H., Lu X., Li H. et al. Association between exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and lipid peroxidation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Science of The Total Environment. 2021. 780. 146660. doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146660.
- Biller J.D., Takahashi L.S. Oxidative stress and fish immune system: phagocytosis and leukocyte respiratory burst activity. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências. 2018. 90. 3403-3414. doi: 10.1590/0001-3765201820170730.
- Sokolovskaya I., Maryukhnich N., Zarytska V., Kyrpychenko O., Nechiporenko V., Pozdnyakova O. et al. The state of lipid exchange and thrombotic link of hemostasis in patients with chronic non-specific inflammatory diseases of genitals. French-Ukrainian Journal of Chemistry. 2019. 7(1). 34-45. doi.org/10.17721/fujcV7I1P34-45.