Резюме
Актуальність. Мікробіом відіграє вирішальну роль у підтримці гомеостазу організму. Мета дослідження: вивчити особливості змін імунологічного статусу та їх зв’язок з дисбактеріозом товстої кишки у хворих з ураженням жовчовивідних шляхів на фоні цукрового діабету (ЦД) 2 типу та ожиріння. Матеріали та методи. У дослідження були включені 54 пацієнти з ЦД 2 типу та ожирінням різного ступеня тяжкості. Сформовані дві групи обстежених пацієнтів із ЦД 2 типу та ожирінням залежно від типу ураження жовчовивідної системи: в І групу ввійшли 24 хворі з хронічним безкам’яним холециститом, а ІІ групу становили 30 пацієнтів із жовчнокам’яною хворобою (ЖКХ). Результати. Визначення кількісного та якісного складу мікрофлори товстої кишки вказує на дисбіотичні зміни у хворих на ЦД 2 типу з ожирінням та ураженням жовчовивідної системи. Більш виражені порушення в кількісному та якісному складі мікрофлори товстої кишки діагностовані в пацієнтів ІІ групи (ЦД 2 типу та ожиріння у поєднанні з ЖКХ). У хворих ІІ групи вірогідно частіше встановлене збільшення кількості Enterobacter (на 14,2 %, р < 0,05), Citrobacter (на 31,8 %, р < 0,01), Staphylococcus (на 16,7 %, р < 0,05), Clostridium (на 11,8 %, р < 0,05) порівняно з пацієнтами І групи. У пацієнтів із ЖКХ при ЦД 2 типу та ожирінні встановлене більш виражене збільшення всіх показників імуноглобулінів. Зростання рівнів IgA та IgG є безперечним доказом активізації гуморальної ланки імунокомпетентної системи організму у хворих з ураженням жовчовивідної системи при ЦД 2 типу та ожирінні. Висновки. У хворих на ЦД 2 типу та ожиріння в поєднанні з ураженням жовчовивідної системи (переважно при ЖКХ) виявлена зміна кількісного і якісного складу мікрофлори товстої кишки (зменшення кількості Bifidobacterium і Lactobacillus та збільшення концентрації Clostridium, стафілококів, Proteus та Klebsiella). Встановлене порушення імунологічного статусу у хворих на ЦД 2 типу та ожиріння в поєднанні з ураженням жовчовивідної системи, що проявляється збільшенням рівнів IgА, IgG, IgМ, IgG та зменшенням показника С3 та С4 у сироватці крові, переважно в пацієнтів із ЖКХ. Збільшення рівня IgА та IgG прямо залежить від зміни кількості Bifidobacterium і Lactobacillus, Staphylococcus, Clostridium, Proteus при мікробіологічному дослідженні фекалій у хворих на ЦД 2 типу та ожиріння в поєднанні з ураженням жовчовивідної системи (переважно ЖКХ).
Background. The microbiome plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis. The purpose of the research was to study the peculiarities of changes in immunological status and their relationship with colonic dysbiosis in patients with biliary lesions on the background of type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) and obesity. Materials and methods. The study included 54 patients with type 2 DM and obesity of varying severity, who underwent a comprehensive examination. Two groups of those examined for type 2 DM and obesity were formed, depending on the type of lesion of the biliary system. Thus, group I included 24 patients with chronic acalculous cholecystitis, and group II consisted of 30 patients with gallstone disease. Results. The results of the analysis of the quantitative and qualitative composition of the colonic microflora indicate dysbiotic changes in patients with type 2 DM, obesity, and lesions of the biliary system. More pronounced disorders in the quantitative and qualitative composition of colonic microflora were diagnosed in patients of group II (with type 2 DM and obesity in combination with gallstone disease). The patients of group II significantly more often developed an increase in the number of Enterobacter (14.2 %; p < 0.05), Citrobacter (31.8 %; p < 0.01), Staphylococcus (16.7 %; p < 0.05), and Clostridium (11.8 %; p < 0.05) compared with the data of group I. More pronounced increase in all immunoglobulin parameters was found in patients with gallstone disease associated with type 2 DM and obesity. At the same time, the increase in IgA and IgG levels, which is indisputable evidence of activation of the humoral part of the body’s immunocompetent system, was found in patients with biliary lesions and type 2 DM and obesity. Conclusions. In patients with type 2 DM and obesity in combination with lesions of the biliary system (mainly gallstone disease), changes in the quantitative and qualitative composition of the colonic microflora (a decrease in the number of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus and an increase in the concentration of Clostridium, Staphylococci, Proteus, and Klebsiella) were detected. Impairment of immunological status in patients with type 2 DM and obesity in combination with lesions of the biliary tract was diagnosed, which manifested in increased levels of IgA, IgG, IgM, IgG and a decrease in serum C3 and C4 in patients with gallstone disease. The increase in IgA and IgG directly depends on the change in the number of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, Staphylococcus, Clostridium, Proteus in the microbiological examination of feces in patients with type 2 DM and obesity in combination with the biliary system (mainly gallstone disease).
Introduction
The microbiome plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis. Recent data provide new knowledge for understanding the interaction between the microbiota and the human organism. However, the vast majority of such studies have analyzed the interactions occurring in the intestinal tract [1, 2]. Cholecystitis and cholangitis are known to be caused by an intestinal bacterial infection [3]. Therefore, the study of the gastrointestinal microbiota, including fecal microflora and bile microbiota, is a necessary element for understanding the processes affecting the biliary system, especially in patients with metabolically associated diseases such as type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) and obesity. Studies indicate that chronic inflammation of the biliary tract is more often caused by infections of intestinal bacteria, in particular E. coli [3].
The functional and morphological state of the hepatobiliary system largely depends on the intestinal microflora. Normally, the gastrointestinal tract has physical (intestinal and mucosal) and chemical (secretory IgA and antimicrobial peptides) barriers that prevent the translocation of bacteria and their toxins toward the liver. Only a small number of bacteria enter the portal vein and reach the liver, but due to the mechanism of immunotolerance, this process is not accompanied by an immune response. When the intestinal barrier is broken, a large number of bacteria and their metabolites enter the liver that can potentiate hepatobiliary inflammation and fibrosis. This principle underlies the hypothesis of intestinal permeability. The portal vein system provides the metabolic link between the intestine and the liver. Inflammatory processes in the intestine lead to disruption of the intestinal barrier (disruption of the enterocytes’ tight junction) and dysbiosis, allow entry into the liver of microorganisms and pathogen-associated molecules, which can cause damage to the hepatobiliary system.
D.M. Giordano et al. (2018) showed the association of dysbiosis with the development and progression of cholangiopathies. According to this study, in patients with cholangiopathies, the composition of the intestinal microflora differs significantly from that in healthy people. Under normal conditions, cholangiocytes that line the bile duct are involved in the formation of the final composition and amount of bile. Under the influence of certain exogenous or endogenous factors, cholangiocytes may undergo some phenotypic changes. Reactive cholangiocytes provoke the release of pro-inflammatory molecules and activate the innate immune response against the activity of microorganisms or products of their activity, which enter the hepatobiliary system through enterohepatic circulation [4]. Intestinal dysbiosis is associated with metabolic disorders, such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 DM. The study of intestinal dysbiosis in metabolically associated diseases and its relationship with immunological status is important for understanding the processes occurring in the lesions of the hepatobiliary tract in this group of patients.
The purpose was to study the peculiarities of changes in immunological status and their relationship with colonic dysbiosis in patients with biliary lesions on the background of type 2 DM and obesity.
Materials and methods
A comprehensive examination of patients was conducted on the clinical basis of the Department of Propaedeutics of Internal Diseases of the Medical Faculty of Uzhhorod National University. The study included 54 patients with type 2 DM and obesity of varying severity, who were treated in the Endocrinology and Gastroenterology Departments of Municipal Non-Profit Enterprise “Andrii Novak Transcarpathian Regional Clinical Hospital”, in the Surgery Department No. 1 of St. Martin Mukachevo Central District Hospital, or were on outpatient observation by district family doctors in the period of 2019–2021 and 2020–2021.
All studies were performed with the consent of patients, and their methodology was in line with the Helsinki Declaration on Human Rights of 1975 as revised in 1983, the Council of Europe Convention on Human Rights and Biomedicine, and the legislation of Ukraine.
The patients were aged from 21 to 65 years, the average age was (49.6 ± 5.3) years; there were 32 males (59.3 %) and 22 females (40.7 %). The control group included 30 healthy individuals. The control group included 18 males (60.0 %) and 12 females (40.0 %) with an average age of (48.3 ± 5.1) years.
All patients were examined using general clinical methods. To verify the diagnosis, attention was paid to the nature of complaints and medical history. In anthropometric research, height and weight were measured, and body mass index (BMI) was calculated. According to WHO recommendations, patients were distributed depending on the BMI, at which BMI of 16.0 or less is considered underweight (a pronounced deficit of body weight); 16.0–18.5 — underweight (insufficient body weight); 18.5–24.9 — normal weight; 25.0–29.9 — overweight; 30.0–34.9 — grade I obesity; 35.0–39.9 — grade II obesity; 40.0 and more — grade III obesity [5].
All patients underwent ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity using conventional methods, with an emphasis on the state of the biliary system. Standard general and biochemical studies were performed in the blood serum with an emphasis on carbohydrate metabolism (glucose, insulin, glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c, %), and glucose tolerance test).
The diagnosis of type 2 DM was established based on the recommendations of the IDF (2005), as well as taking into account the criteria of a unified clinical protocol (Order of the Ministry of Health of Ukraine No. 1118 of 21.12.2012) [6, 7]. The severity of type 2 DM was assessed by the level of HbA1c (normal: up to 6.0 %).
Patients underwent fecal analysis for dysbiosis, with quantitative determination of microorganisms grown on agar, Sabouraud, Endo, and 5% blood agar in 1 g of feces. Besides, hemolytic forms of both intestinal and coccal microflora, the percentage of total colonies grown, and the ratio of intestinal and coccal microflora were determined on a 5% blood agar plate. The presence of Bifidobacteria was determined by the nature of growth on Blaurock medium and microscopy of Gram-stained smears. The number of Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli per one gram of feces was determined by the limiting dilution at which their growth was observed. The degree of intestinal dysbiosis was assessed according to the classification of I.B. Kuvaieva, K.S. Ladodo (1991).
The levels of C3, C4 complement components and the concentration of immunoglobulins (Ig) A, M, G were determined using chromogenic analysis on the Sysmex 500 and 560 (Japan) with Siemens reagents.
Two groups of those examined for type 2 DM and obesity were formed, depending on the type of lesion of the biliary system. Thus, group I included 24 patients with chronic acalculous cholecystitis, and group II consisted of 30 patients with gallstone disease.
The exclusion criteria were: type 1 DM, type 2 DM in the decompensation stage, normal and overweight, history of cholecystectomy.
Analysis and processing of the examination results of patients were carried out using Statistica 10.0 (StatSoft Inc., USA) computer program by parametric and non-parametric methods for evaluating the results.
Results
After clinical and laboratory tests, all patients were diagnosed with type 2 DM, mostly mild to moderate, in combination with obesity of varying severity.
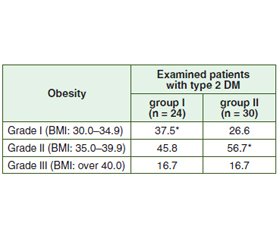
Anthropometric examination of patients of both groups revealed obesity of grade II more often. In patients of group II, it was 10.9 % more frequent than in patients of group I (p < 0.05). Obesity of grade I was more common in patients of group I (37.5 % of subjects; p < 0.05) (Table 1).
The results of the analysis of the quantitative and qualitative composition of the colonic microflora indicate dysbiotic changes in the colon in patients with type 2 DM, obesity, and lesions of the biliary system. This manifested in a decrease in the frequency and number of Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, Escherichia, Enterococcus, and an increase in the frequency of detection of Staphylococcus, Klebsiella, Proteus, Clostridium, and Candida compared with the control group in patients of both study groups (Table 2).
/23.jpg)
At the same time, more pronounced disorders in the quantitative and qualitative composition of colonic microflora were diagnosed in patients of group II (patients with type 2 DM and obesity in combination with gallstone disease). The patients of group II significantly more often developed an increase in the number of Enterobacter (14.2 %, p < 0.05), Citrobacter (31.8 %, p < 0.01), Staphylococcus (16.7 %, p < 0.05), and Clostridium (11.8 %, p < 0.05) compared with the group I patients. Also, patients in group II significantly more often experienced a decrease in the number of Lactobacillus (by 13.3 %, p < 0.05), Escherichia with normal enzymatic properties (by 10.8 %, p < 0.05), and Enterococcus (by 13.3 %, p < 0.05) compared with patients in group I.
Changes in the quantitative and qualitative composition of colonic microflora in those with lesions of the biliary system on the background of type 2 DM and obesity were also accompanied by changes in immunoglobulin levels and complement parameters in serum (Table 3).
In patients with chronic acalculous cholecystitis and gallstone disease on the background of type 2 DM and obesity, an increase in serum IgA levels was found, with the most pronounced deviation from the norm in patients of group II. An increase in serum IgM and IgG was also diagnosed in both groups of examined patients. Also, a more pronounced increase in all immunoglobulin parameters was found in patients with gallstone disease associated with type 2 DM and obesity. At the same time, the increase in IgA and IgG levels, which is indisputable evidence of activation of the humoral part of the body’s immunocompetent system, was found in patients with biliary lesions, type 2 DM, and obesity. Decreases in the C3 and C4 parameters of the complement system were also observed in both groups of the examined patients.
A correlation analysis was performed to determine the relationship between the species composition of the colonic microflora and indicators of the immunological status of the organism in the examined patients (Table 4).
The relationship between a decrease in the amount of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus and an increase in the concentration of IgA and IgG, as well as the level of complement C3 in patients with gallstone disease (group II), was found. In patients of group I, the amount of Lactobacillus also correlated with IgA, IgG, and C3 levels. There was a correlation between the increase in the number of Staphylococci in the composition of the colon microflora and the level of IgA, IgG in patients of group II, and a negative relationship with complement C3. The increase in the level of Clostridium directly affects the IgA serum level in both groups of examined patients. There was also a correlation between Proteus and IgA and C3 levels mainly in patients of group II.
Discussion
In recent years, numerous studies have shown that biliary tract diseases and chronic liver diseases are affected by microbiota. Much attention has been paid to the study of intestinal microbiota as it has been shown that proinflammatory cytokines enter the liver through enterohepatic circulation and cause liver inflammation. However, the suggestion that the biliary system itself may contain a complex microbiota opens a discussion about the possible links between biliary dysbacteriosis and inflammatory diseases of the biliary and hepatocellular systems. Studies of the biliary microbiota show that chronic diseases are associated with extensive changes in microbial content. Knowledge of the influence of intestinal and biliary microflora on biliary tract disorders is important not only for a better understanding of the etiology of these diseases but can also provide therapeutic solutions in the future [8].
The results of our studies showed pronounced changes in the quantitative and qualitative composition of the colonic microflora in patients with biliary tract disease on the background of type 2 DM and obesity. Moreover, more pronounced changes in the composition of feces were found in gallstone disease than in chronic acalculous cholecystitis on the background of metabolic changes. The analysis of the results indicates a decrease in the number of Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli, as well as an increase in Clostridium, Proteus, and Staphylococci. T. Wu, Z. Zhang et al. (2013) also found that the composition of the intestinal microflora in patients with gallstone disease differs from the composition of the microflora in healthy people. Thus, an increase in the number of proteobacteria Escherichia, Salmonella, Helicobacter spp. and reduction of Faecalibacterium, Lachnospira, Roseburia spp. were found in patients with gallstone disease [9]. The works of Liu et al. (2015) indicate that E. coli is the main pathogen of the biliary tract, among others, such as Klebsiella spp., Clostridium perfringens, Citrobacter freundii, and Enterobacter cloacae. Besides, the amount of bile endotoxin significantly correlated with the number of Enterobacteriaceae, especially Escherichia coli. Enterobacteriaceae may play a significant role in the pathogenesis and/or progression of acute cholecystitis. Kose et al. (2018) in the analysis of pigmented stones found that the formation of the biofilm involved mainly pathogenic Klebsiella and Enterococci. Klebsiella was also present in one of the cholesterol gallstones, while the other cholesterol stones analyzed showed a predominance of Gram-positive bacteria that were not detected in the pigmented stones [1].
However, despite the many studies conducted, the scientific community has not yet succeeded in finding out whether colonic dysbiosis is a consequence of gallstone disease or vice versa. The further study of the immunological status of patients with lesions of the biliary system in metabolically induced diseases is of particular interest. The proven link between the intestinal microflora and the hepatobiliary system opens another goal of therapeutic effect in the complex treatment of patients with biliary tract disorders, aimed at correcting dysbiosis, especially in patients with type 2 DM and obesity.
Conclusions
1. In patients with type 2 DM and obesity in combination with lesions of the biliary system (mainly gallstone disease), changes in the quantitative and qualitative composition of the colonic microflora (a decrease in the number of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus and an increase in the concentration of Clostridium, Staphylococci, Proteus, and Klebsiella) were detected.
2. Impairment of immunological status in patients with type 2 DM and obesity in combination with lesions of the biliary tract was diagnosed, which manifested in increased levels of IgA, IgG, IgM and a decrease in serum C3 and C4 in patients with gallstone disease.
3. The increase in IgA and IgG directly depends on the change in the number of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, Staphylococcus, Clostridium, Proteus in the microbiological examination of feces in patients with type 2 DM and obesity in combination with the disorders of the biliary system (mainly in patients with gallstone disease).
Received 02.11.2021
Revised 11.11.2021
Accepted 18.11.2021
/22.jpg)

/23.jpg)
/24.jpg)